

Subbing in s = -10 and a = -9.8 gives t = 1.429 seconds, this is the time it takes the ball to reach the floor. In this case, we want to find t and we have u, a and s, so we use Eqn 2: This is done by looking at the suvat list and comparing to the equations above. The next step in this solution is to use the vertical suvat equations to calculate the time it takes the ball to reach the ground.
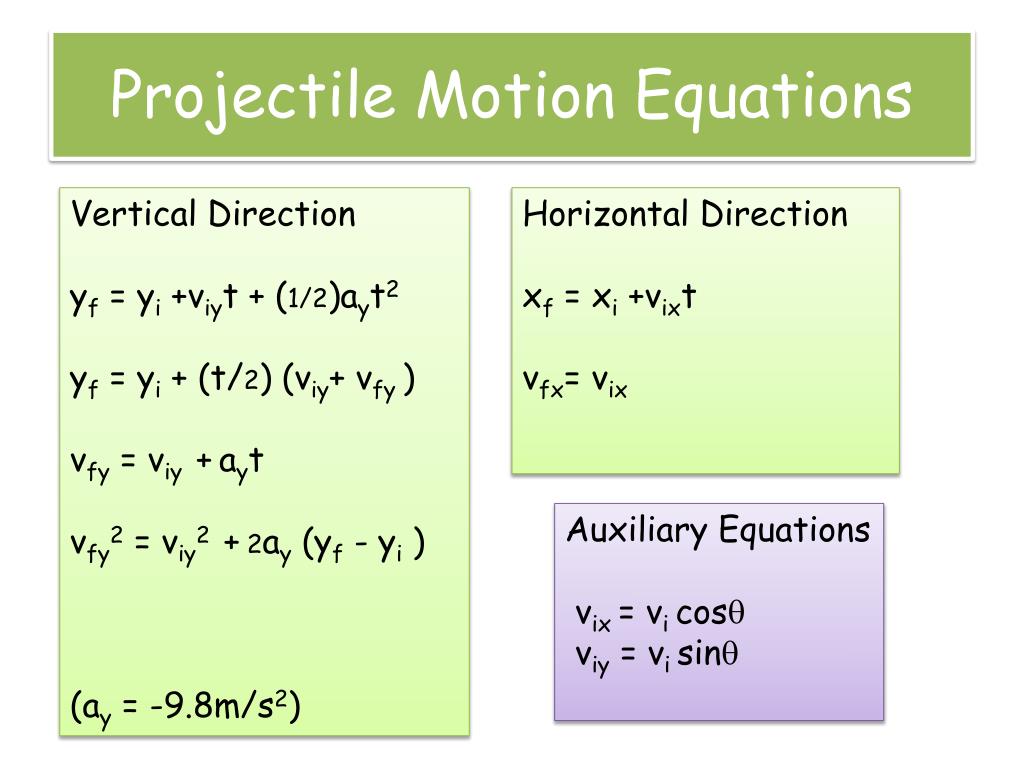
Remember that displacement is a vector so the vertical displacement is the height with a minus sign in front of it to show that the ball has dropped this height. there is no vertical component when t=0, the vertical component only occurs because of acceleration due to gravity as the object falls). The inital vertical component of velocity is 0 as the object is thrown vertically (ie. In this case, the gravitational force creates an acceleration due to gravity equal to -g, where g = 9.8ms -2. So far, we don't know any other horizontal values. Note that because gravity is the only force acting on the projectile and this is a vertical force, there is no horizontal force and hence no acceleration in the horizontal direction, so the intial and final velocities remain the same. So we begin by writing out the suvat lists for each component: As a result, when writing out our 'suvat' equations, we must have separate equations for the horizontal and vertical components.

The first step in all projectile motion questions should be to understand that the velocity of the object being thrown, in this case the ball, has 2 components, its vertical component and its horizontal component. Calculate the time it takes to drop to the floor and its horizontal displacement at the point when it reaches the floor. Where s = displacement, u = initial velocity, v = final velocity, a = acceleration and t = timeĪ ball is thrown from the top of a 10m high building with a horizontal speed of 5ms -1. A projectile is an object which is moving under its own inertia - in simpler terms, t he only force acting upon it is gravity.įor this example, the following 'suvat' equations are used: In this question, we deal with the case that the projectile is horiontally launched.īefore attempting to answer projectile motion questions, it is important to understand what a projectile is. There are 2 types of typical projectile motion questions: horizontally launched projectiles (in which an object is launched horizontally from an elevated plane and follows a parabolic path to the ground) and non-horizontally launched projectiles (in which an obect is thrown in the air from the ground, rises to a peak height and then drops to the ground again). Projectile motion questions are common in A-level physics as they combine the idea of resolving vectors into their components and using the equations of motion ('suvat' equations) to calculate unknown quantities relating to an object's motion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
